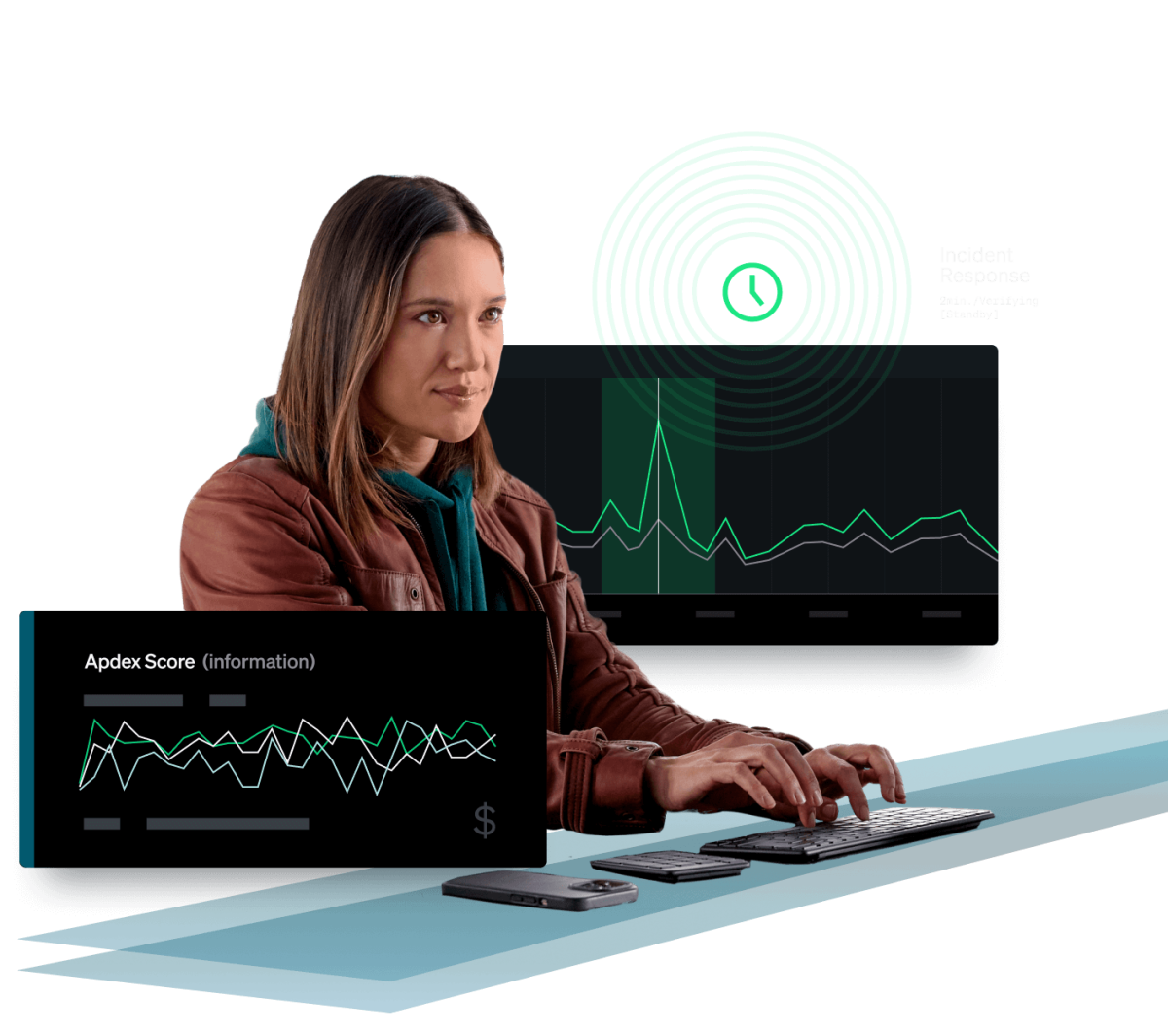
Troubleshoot, debug, and optimize on one platform.
Monitor performance now—with automatic agents or OpenTelemetry.
- Start fast with 525+ integrations, including automatic instrumentation for popular languages and frameworks.
- Instantly monitor golden metrics, visualize dependencies, and set up alerts to stay a step ahead.
- Ingest your way—with New Relic agents or with full support for OpenTelemetry.
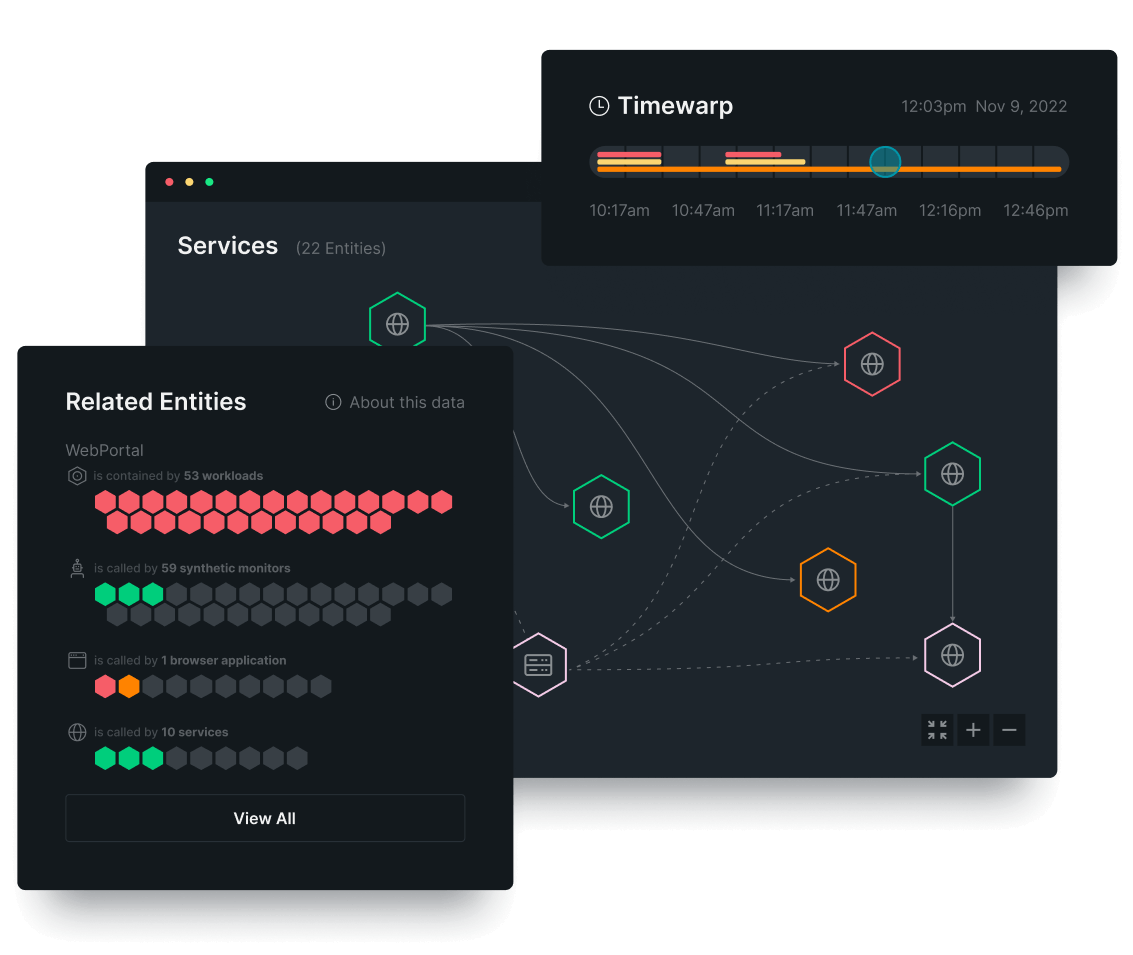
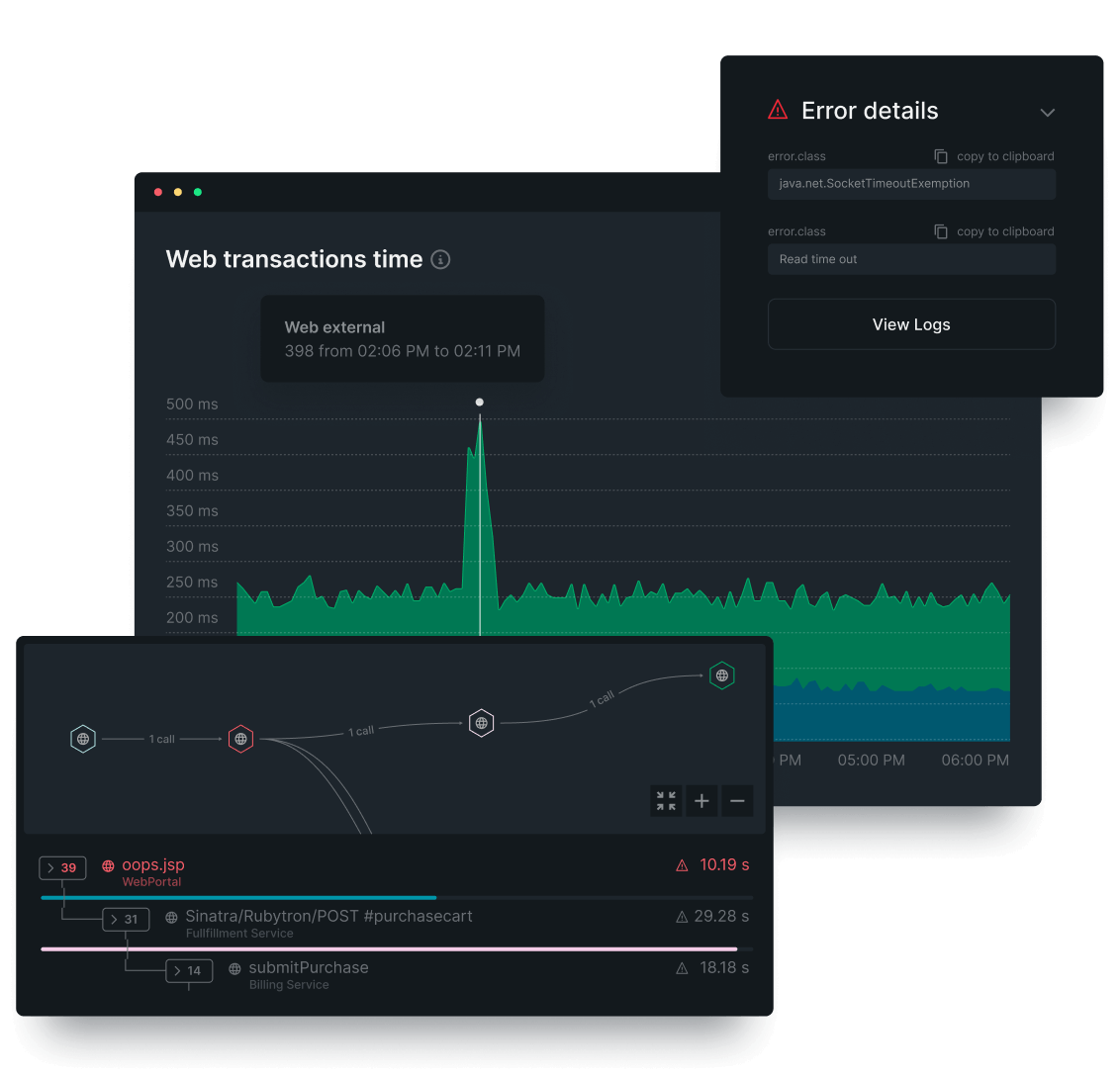
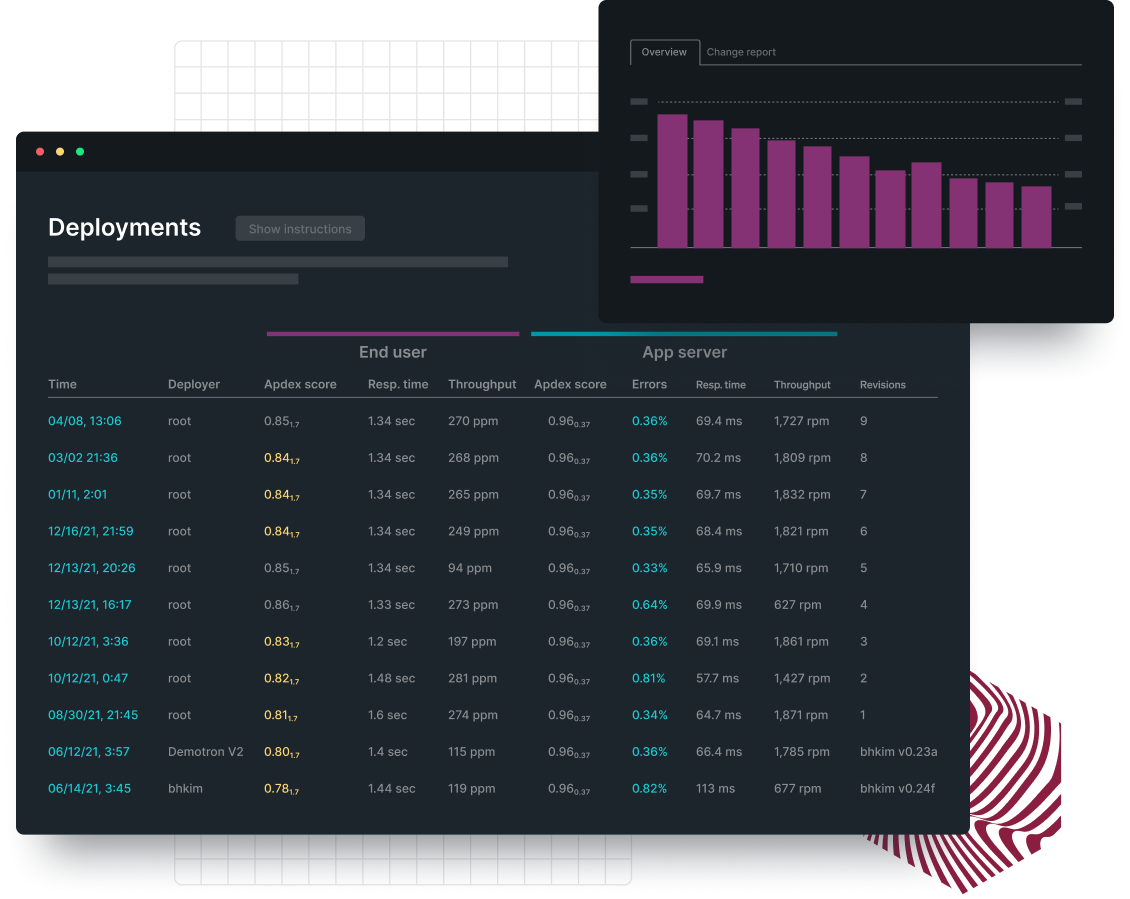
Debug faster with all your telemetry in one place.
- Untangle complexity by using distributed tracing to visualize the path of any service request.
- Stay focussed by viewing application logs in context with APM metrics, traces, and events.
- Find the root cause faster with errors tracking, change tracking, and AIOps.
- Learn how William Hill resolves issues 80% faster.
Improve systems and workflows—for every engineer.
- Monitor SLAs and business KPIs in real time to resolve issues before they impact your users or business.
- Gain instant visibility into all application vulnerabilities with no additional configuration.
- Improve team efficiency and process by bringing telemetry to engineers in their IDEs.
- Learn how PicPay reduces incident volume 60%.
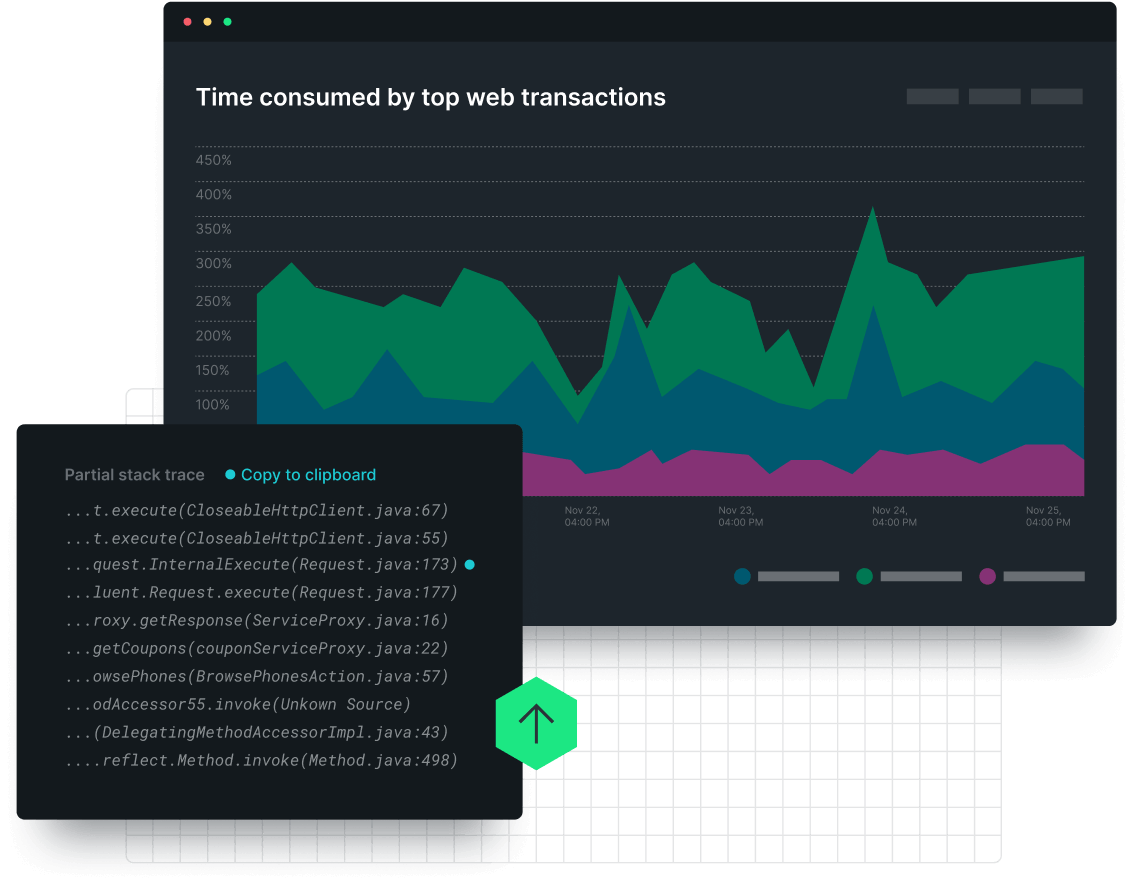
Pay for actual usage, not peak usage.
- Simple, transparent pricing suited for modern applications.
- Consolidate tools, remove silos, and control costs with next-gen APM.
- 30+ capabilities integrated with APM for one price on the all-in-one observability platform.
Ready to start quickly?
Instrument everything in a few clicks with quickstarts from New Relic Instant Observability.
has us open.
30+ Capabilities. One platform.
One price.
Customer Stories
Application Performance Monitoring FAQs
APM stands for "application performance monitoring." It's a set of tools and processes used to monitor and optimize the performance of software applications. APM systems can track various metrics, such as response times, resource usage, and error rates. This provides insights into how to improve the performance of an application.
The aim is to help organizations detect anomalies, reduce latency, and optimize the customer experience. APM can also be used to detect and diagnose problems, such as bottlenecks or bugs, that may be impacting the performance of an application.
There are several ways to assess the performance of an application. APM strategies and tools alert your dev teams of errors and issues before customers experience them.
With APM software, you can assess your application’s performance from one dashboard. Here are the most common assessment methods:
1. Monitoring: This involves collecting data on various performance metrics, such as response times, resource usage, and error rates, and then analyzing that data to identify trends and potential issues.
2. Load testing: This involves simulating real-world usage scenarios, such as a large number of users accessing the application at the same time, to see how the application performs under stress.
3. Performance profiling: This involves analyzing the application's code to identify bottlenecks or areas that could be optimized for better performance.
4. User feedback: This involves collecting feedback from users about their experiences using the application, including any issues they may have encountered.
5. A/B testing: This is a method of comparing two versions of an application to see which one performs better.
6. Synthetic monitoring: This is a method of monitoring an application's performance by simulating user interactions with the application in a controlled environment.
There are several key metrics that you should monitor when using APM tools:
1. Response time: This measures how long it takes for a request to be processed and a response to be returned.
2. Error rate: This measures the number of errors that occur in the application, such as failed requests or unhandled exceptions.
3. Resource usage: This measures the amount of system resources, such as CPU and memory, that the application is using.
4. Throughput: This measures the number of requests that the application can handle within a certain time period.
5. Latency: This measures the time it takes for data to travel from the client to the server and back.
6. User experience: This measures the overall satisfaction of the users with the application.
7. Business metric: This measures the impact the application has on the business, such as the number of transactions, revenue, conversion rate, etc.
It's important to monitor these metrics over time to detect trends and patterns, and to be able to identify when and where performance issues occur in the application.
Also, it's important to note that depending on the specific requirements of your application, you may need to monitor additional or different metrics.
There are several benefits to using APM software.
1. Your users will have a better experience. By monitoring the performance of an application, APM software can provide insights into how to improve the user experience. This can help organizations ensure their applications are running smoothly and providing good user experience.
2. Your app will have increased reliability. APM software can detect and diagnose problems, such as slow response times or high error rates, that may be impacting the reliability of an application. By addressing these issues, the reliability of the application can be increased.
3. APM software can save money by helping organizations identify and address performance issues before they cause major problems, such as system downtime or lost revenue.
4. You can create better business performance. APM software can provide detailed information on how the application is impacting the business, such as the number of transactions, revenue, conversion rate, and other key business metrics. This information can be used to optimize the application and improve the overall business performance.
Overall, APM software can help organizations ensure that their applications are running smoothly, providing a good user experience, and impacting the business positively.
There are several ways to monitor application performance in production. Application performance in production combines several factors, including:
1. Real user monitoring (RUM): This involves collecting data on the performance of the application as it's being used by actual users. This can be done by using JavaScript tags that are embedded in the application's code to collect data on the client side, or by using proxy servers to collect data on the server side.
2. Synthetic monitoring: This involves simulating user interactions with the application in a controlled environment, such as a test server, to measure performance.
3. Log analysis: This involves analyzing log files generated by the application to identify performance issues, such as slow response times or high error rates.
4. Application instrumentation: This involves adding code to the application to collect data on performance metrics, such as response times and resource usage, that can be used for monitoring.
5. Infrastructure monitoring: This involves collecting data on the performance of the underlying infrastructure, such as servers and network devices, that the application is running on.
6. Third-party tools: There are several third-party tools that can be used for monitoring application performance in production, such as APM tools.
APM software can help monitor all of these factors in one dashboard so you don’t have to run various different tests to get a holistic view of the app environment.
There are several ways to measure application performance:
1. Response time: This measures how long it takes for a request to be processed and a response to be returned. It's typically measured in milliseconds.
2. Error rate: This measures the number of errors that occur in the application, such as failed requests or unhandled exceptions. It's typically measured as a percentage of total requests.
3. Resource usage: This measures the amount of system resources, such as CPU and memory, that the application is using. It's typically measured in bytes or percentages.
4. Throughput: This measures the number of requests that the application can handle within a certain time period. It's typically measured in requests per second or transactions per minute.
5. Latency: This measures the time it takes for data to travel from the client to the server and back. It's typically measured in milliseconds.
6. User experience: This measures the overall satisfaction of the users with the application. It can be measured through surveys, user feedback, and other user-centered metrics.
Your IT and DevOps teams can measure app performance by using data gathered on abnormalities and performance issues. This data is easily rendered in APM software that's already monitoring performance factors like this. Using this data, you can comprehend trends, optimize resource use, and resolve performance issues before they impact end users.